

Login
Assignment
| Aim of method usage: |
|---|
|
| Method classification: |
|
| Process phase: |
|
Useful links:
| Glossary |
| Privacy Policy |
| Literature |
Value Analysis
DIN 69910
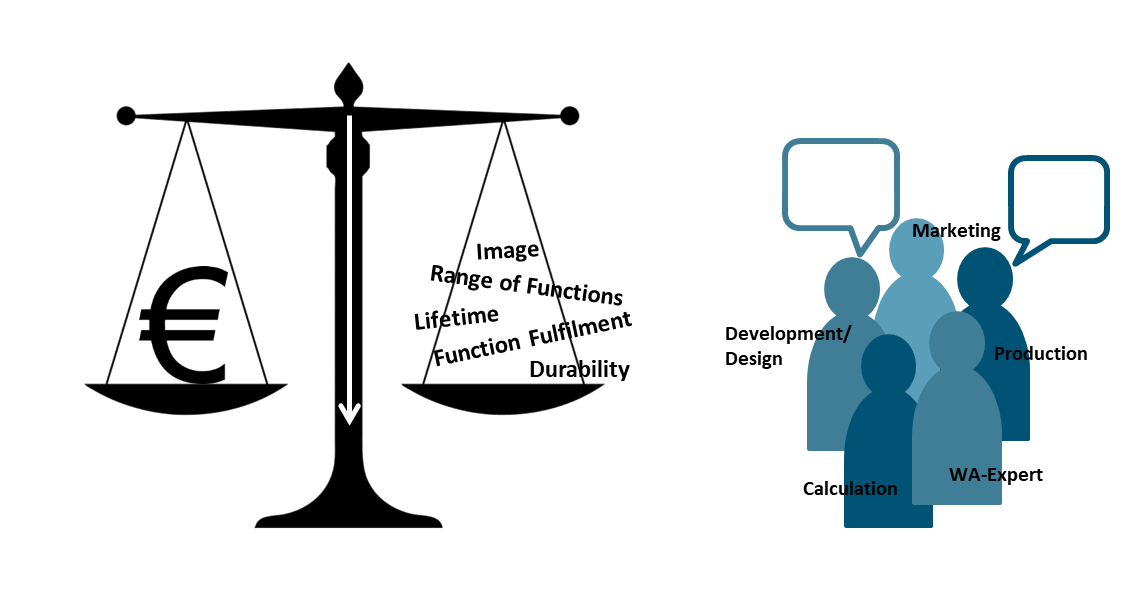
In value analysis a group of experts is tasked with systematically analyzing an objects functions and referring to ist specific costs.
The goal is to offer possibilities as to how the relation between costs and use expected from the customer can be optimized.
The procedure to analyze the object situation will be discribed in the following cells.
Procedure
- Preparation of project: Preparing the project includes the formation of an interdisciplinary expert group, the nomination of a moderator, the fixation of general and specific goals, the limitation of the investigative scope and the planning of the project organization as well as the proceedings.
- Gathering information about project and surroundings: If the object situation is to be analyzed, information on the project and its surroundings need to be gathered using for example construction documents, requirement lists, etc.
- Gathering information on costs: One may find information on costs using data from controlling, cost structures orsales figures.
- Identifying functions: To identify the functions of a technical system, one needs to divide the overall function required into partial functions of decreasing complexity and formulate it as an object-predicate construction (e.g take on axial forces). Then the corresponding functionaries are set (assembly, component).
- Matching functional classes: All functions are divided into functional classes and types. The functional classes are used to establish a ranking; there are the classes main/ secondary/ unfavored functions as well as the types functionability and validity.
- Identifying solutions depending on requirements: All requirements or boundary conditions that influence or limit the solution need to be identified.
- Matching costs and functions: For each determined function the cost needs to be calculated. The function costs are the basis for evaluating concepts or design options since the costs need to be minimized up to the point where somewhat unnecessary functions will be eliminated.
- Description of target state: Evaluating the gathered information leads to target functions that are matched with cost objectives.
- urther steps: Solution ideas need to be developed further so that solutions can be formulated and realized.
Strengths and weaknesses
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
| go back |
zur Startseite



