Module Indication Matrix
Modular Function Deployment (MFD), MIM
Die Modul Indication Matrix (MIM) ist eingebettet in die Methodik Modular Function Deployment (MFD). Hierbei werden zunächst mithilfe einer QFD-Methodik die Kundenbedürfnisse geklärt. Davon ausgehend werden Funktionen analysiert und technische Lösung ausgewählt. Im nächsten Schritt kommt die hier vorgestellte MIM zur Identifikation von möglichen Modulen zum Einsatz. Anschließend kann jedes Modul beispielsweise mittels Design for Manufactioring and Assemlby (DFX) verbessert werden.
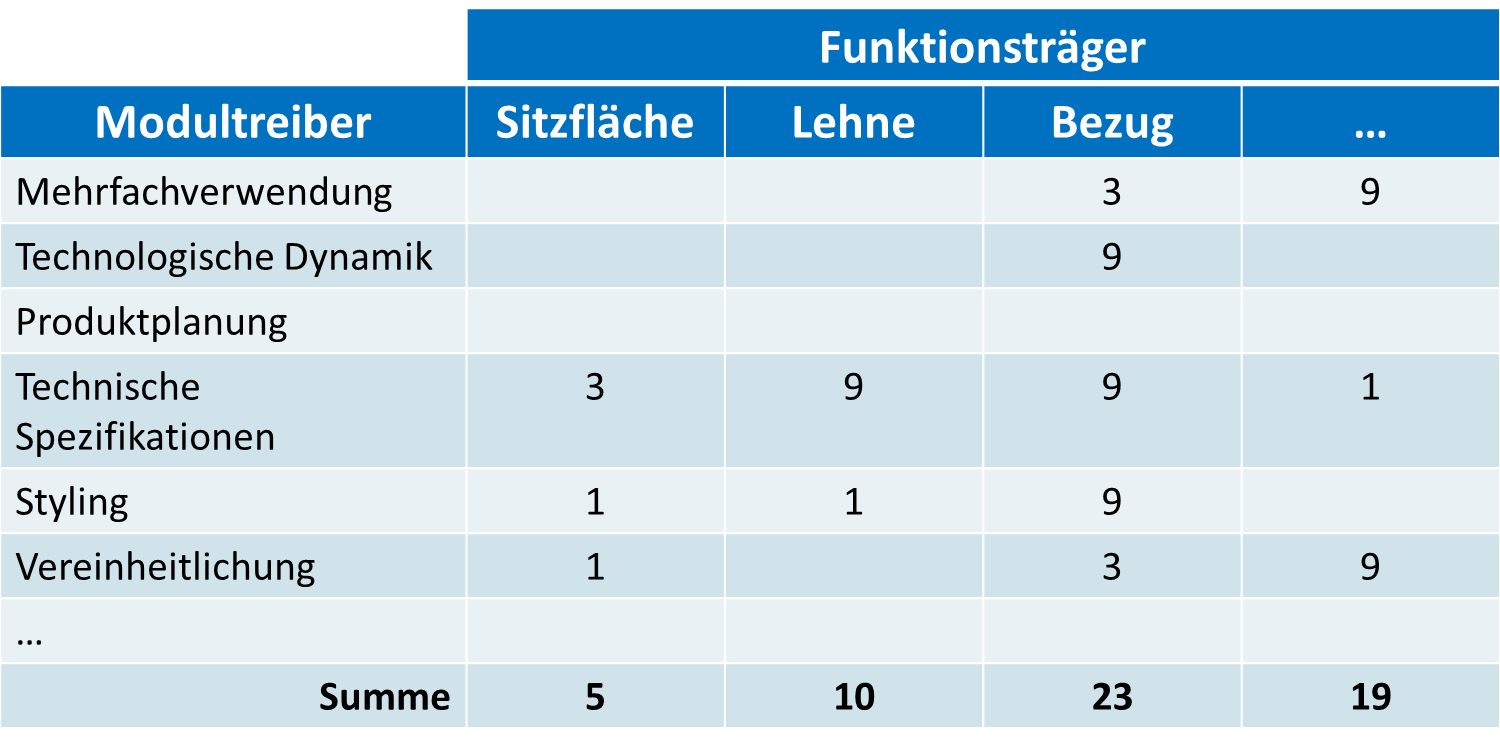
Die Module Indication Matrix dient zur Identifikation von Modulkandidaten für die modulare Produktarchitektur. Dies erfolgt über die Analyse der Funktionsträger mithilfe von Modultreibern. Die Funktionsträger werden nach einer Gegenüberstellung mit den Modultreibern bewertet.
Vorgehensweise
- Erfassen der Modultreiber: Sämtliche oder die zu berücksichtigenden Modultreiber eines Produktes werden ermittelt.
- Erfassen der Funktionsträger: Sämtliche oder die zu berücksichtigenden Funktionsträger eines Produktes werden ermittelt.
- Korrelation zwischen Modultreibern und Funktionsträgern: In diesem Schritt wird der Zusammenhang zwischen Modultreibern und Funktionsträgern systematisch untersucht. Es wird geprüft, ob eine Beziehung besteht, und die entsprechende Stärke (keine, schwache, mittelstarke oder starke Beziehung) wird dokumentiert. Es gibt die Möglichkeit eine lineare (z.B. 0,1,2,3) oder eine progressive Skala (z.B. 0,1,3,9) zu wählen.
- Auswahl der Modulkandidaten: Für die Funktionsträger werden die vergebenen Korrelationswerte aufsummiert. Aufgrund dieser Werte kann die Wahl eines Modulkandidaten erfolgen.
Stärken und Schwächen
|
Stärken
|
Schwächen
|
- fördert Übersichtlichkeit über Modulkandidaten
- verbessert Modularisierung
|
- Funktionsträger müssen vollständig bekannt sein
|







