

Login
Assignment
| Aim of method usage: |
|---|
|
| Method classification: |
|
| Process phase: |
|
Useful links:
| Glossary |
| Privacy Policy |
| Literature |
Defects Analysis
Defects analysis is used to structurally do damage assessment. The reasons for the defect (malfunction or failure) are traced back through the product's life course and the underlying product principle.
The starting situation is usually a complaint or a defect. First the facts need to be clarified and immediate actions defined. Then the next step can be the systematic defects analysis.
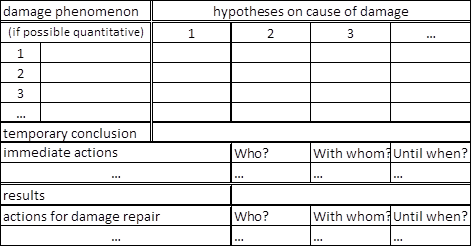
Procedure
- Group formation for defect repair: assemble a group of experts to analyze the defect.
- Damage phenomena: damage phenomena, observations and statements of parties envolved need to be collected on a data sheet.
- Hypothesizing and reevaluating: for each phenomenon or observation one formulates multiple hypotheses regarding the cause for the defect or observation.
- Preliminary result: the experts formulate their preliminary findings.
- Extrapolation of immediate actions to correct the defect: immediate actions and people responsible are defined as well as a time frame.
- Results and further actions: the results of the immediate actions are documented and their effectiveness analyzed. Based on that, further actions for correcting the defect are formulated.
- Post-processing/ documentation: the entire process needs to be thoroughly documented and finished so that the findings may be used for all further defects as well as to provide legal security.
Strengths and weaknesses
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
|
|
| go back |
zur Startseite



